ETH: The Internet Finance Bond
Level up your crypto finance game five times a week. Get on the Bankless Program.
The economics of Ethereum
Dear Bankless Nation,
And the launch of Eth2 staking is like the bond offering for the decentralized economy. A decentralized, global economy entirely built on the internet.
And people are just starting to wrap their heads around it.
Our friends Collin Myers and Mara Schmiedt just published a full whitepaper and a financial model on Eth2 and its economics.
They modeled staked ETH as a bond. This model helps investors understand ETH as a revolutionary new internet native asset type through the lens of assets they already know—perpetual bonds.
We love it so much we teamed up with them to put together an executive summary.
Welcome to the dawn of the internet bond.
- RSA
🙏Sponsor: Aave—earn high yields on deposits & borrow at the best possible rate!
THURSDAY THOUGHT
Guest Post: Collin Myers of ConsenSys & Mara Schmiedt of Bison Trails
ETH: The Internet Bond
A Whitepaper on Digital Work Agreements in the Web3.0 Era
Until the invention of public blockchain networks, it has not been easy for entities or individuals to directly participate in or obtain financial exposure to the base layer of the internet.
The arrival of Web3.0 changes this. Now, it’s possible for participants anywhere in the world to get exposure to the open-source web economy through a new generation of digital work agreements—Internet Bonds.
Understanding the fundamental properties of this new type of agreement is a critical first step in creating better models, valuation and products around it. In a matured state, the yield of the internet’s new settlement layer can become the risk free rate of a decentralized financial ecosystem and a benchmark for valuing the cost of trustless value transfer.
As internet bonds grow in popularity, creating a shared terminology and understanding around them will be critical to global adoption.
📑 Read the full Internet Bonds whitepaper here
What are Internet Bonds?
Today, the most popular digital work agreements involve collateralizing value for the right to provide work and earn rewards. This is widely known as ‘staking’.
Similar to traditional bond structures, staking comes in a variety of flavors, but at its core represents an agreement between the bond issuer (the protocol) and the bond holder (the validator or delegator).
Let’s draw an analogy from the non-digital world.
In many parts of the world, construction professionals are required to purchase a contractor license bond before they are legally allowed to provide construction work. By purchasing the contractor license bond, the construction professional agrees to work in accordance to rules and regulations designed to protect both the government agencies and consumers from potential financial loss.
A contractor license bond is a type of surety bond between:
- The Principal: the entity seeking permission to work by offering capital and consenting to set of rules
- The Obligee: the entity setting the requirement for the bond in adherence to a set of rules and surety
- The Issuer: the entity guaranteeing the obligations of the principal
In the world of crypto and Proof of Stake, staking bonds can be viewed as a type of contractor license bond. Ethereum Validators, for example, are required to stake 32 ETH as collateral to register their node on the network and in return obtain the ‘license’ to support consensus operations on-chain.
By obtaining this license, the validator agrees to adhere to the network’s rules, which is to behave honestly and guarantee continued operations. In return, they receive periodic rewards.
The bond in this case is an agreement structured between:
- The Principal i.e. the Validator
- The Obligee and Issuer i.e. the Ethereum Blockchain
In this example, Ethereum acts as both the obligee and the issuer. That is, it programmatically defines and enforces the rules defined to maintain the network’s integrity. Validators that fulfill their obligations earn rewards as an incentive for doing so, while those who do not meet their operative requirements or behave maliciously run the risk of incurring penalties, forfeitures and/or lose the right to participate (‘slashing’).
Therefore, staking positions can, in an abstracted sense, be thought of as a Web3.0 digital work agreement which resembles and shares similar behavioral patterns with bond structures in the traditional financial world.
So what’s the main difference?
Holders of the Internet Bond in Web3.0 are lenders of capital, labor, and owners of the network all at the same time.
As a result, an Internet Bond is a new type of incentivized digital work agreement that, in a mature state, can be best described as a hybrid-perpetual bond with debt and equity like characteristics. 🔥
Eth2 Internet Bonds - An Ether price analysis
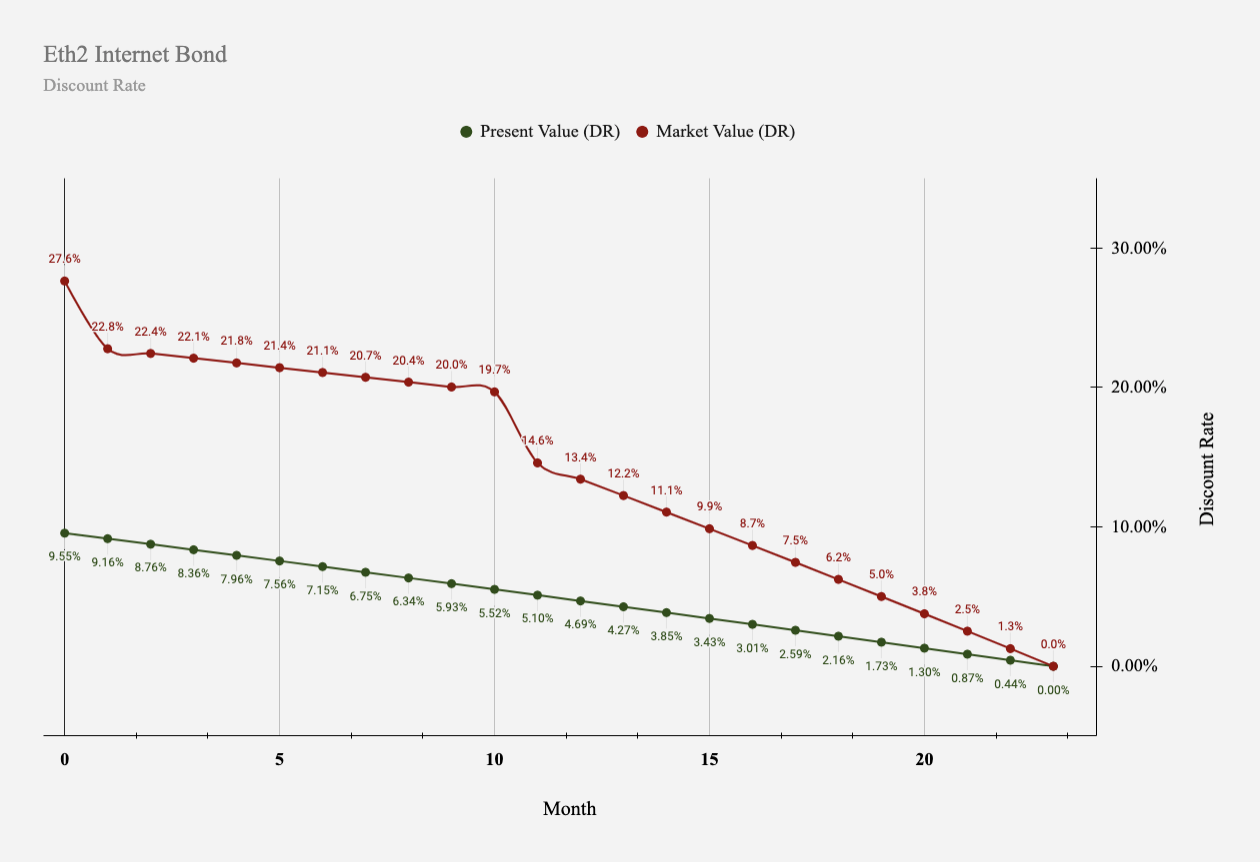
Eth2 Internet Bonds behave like evolutionary assets, due to the nature of open source software and the evolving redemption properties tied to the phased roll out of Eth2.
The whitepaper we published uses the Ethereum 2.0 protocol to demonstrate the application of the proposed conceptual framework to better understand, value, and project the market for participation in Ethereum 2.0.
Specifically, the paper focuses on the early phases of Eth2 and forecasts what an Eth2 Internet Bond may look like. Areas of focus are:
- Value
- Rewards
- Network State
Modeling the Behaviour of eth2 Internet Bonds
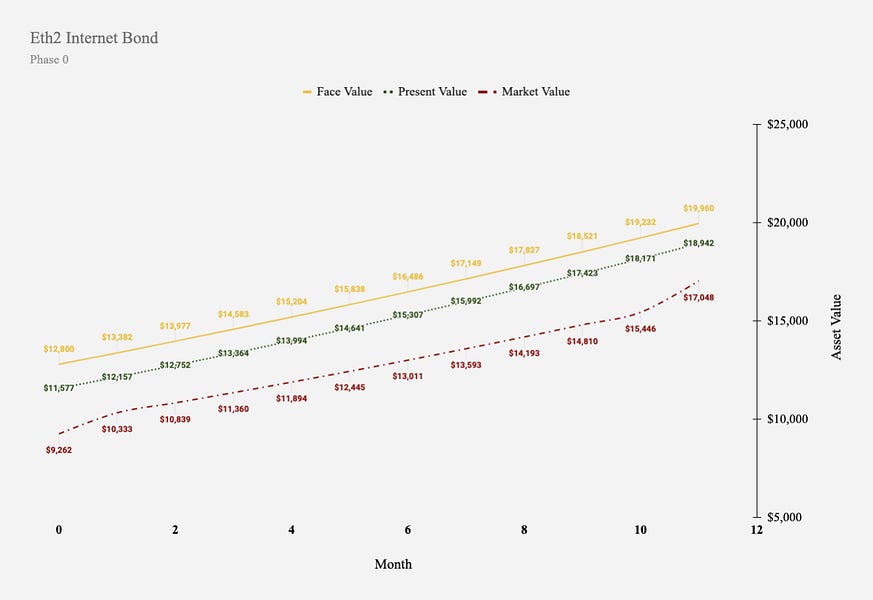
With the recent launch of the deposit contract, validators can now deposit 32ETH directly to the protocol or do so in fractional increments through a custodial intermediary. Deposits are done through a one-way transaction to a smart contract on the Eth1 chain. As Phase 0 is intended to serve as an initial bootstrapping phase, both initial deposits and accrued rewards will be transfer-restricted until Phase 1.5.
As a result, we are able to start with the blueprint of the Eth2 Internet Bond as a deferred reward agreement. Most notably, a deferred interest bond is a debt agreement with accrued interest only paid in full upon maturity. Deferred interest instruments are typically issued and trade at a deep discount to compensate holders for this period of deferred returns and illiquidity. As a result, the value of the asset eventually converges to face value upon maturity.
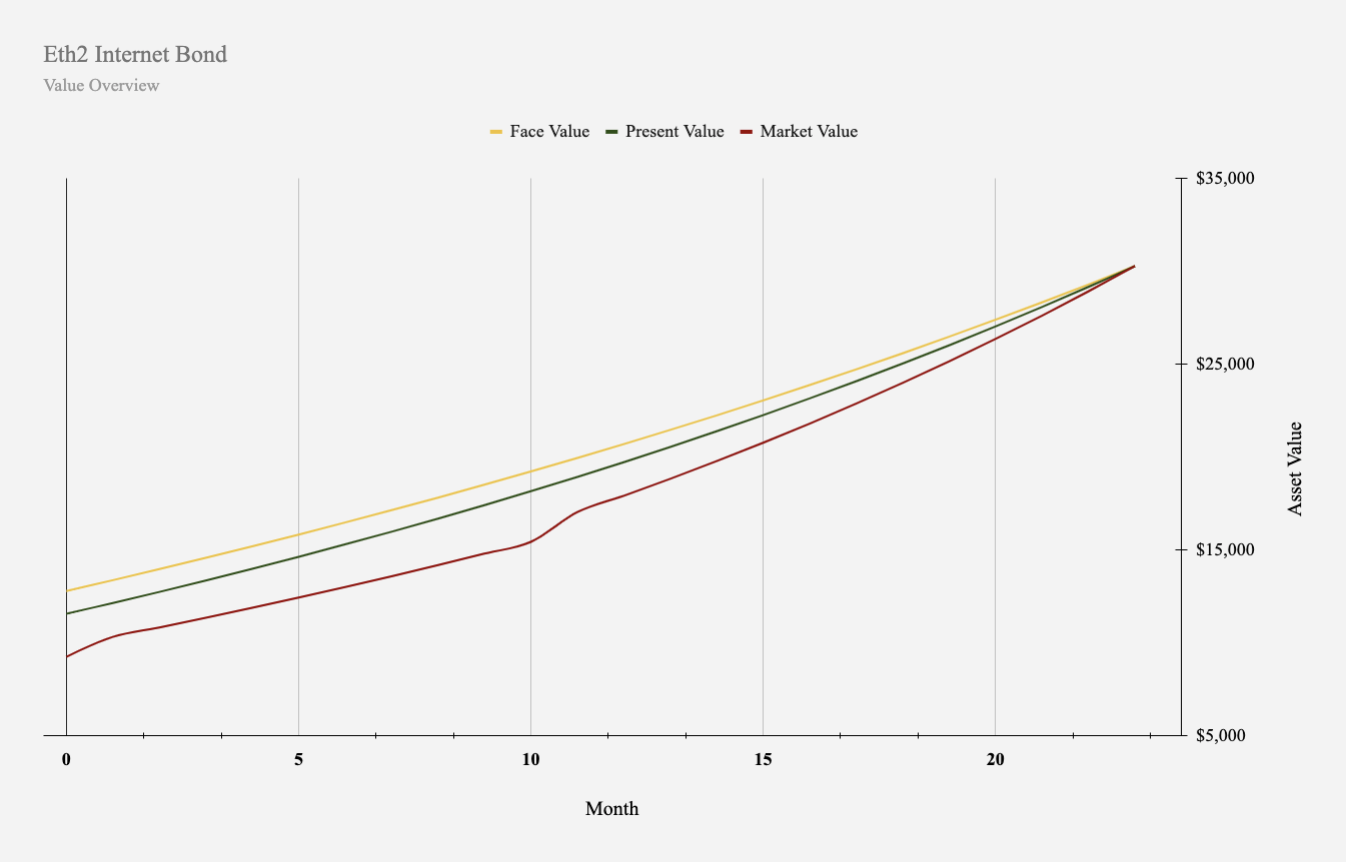
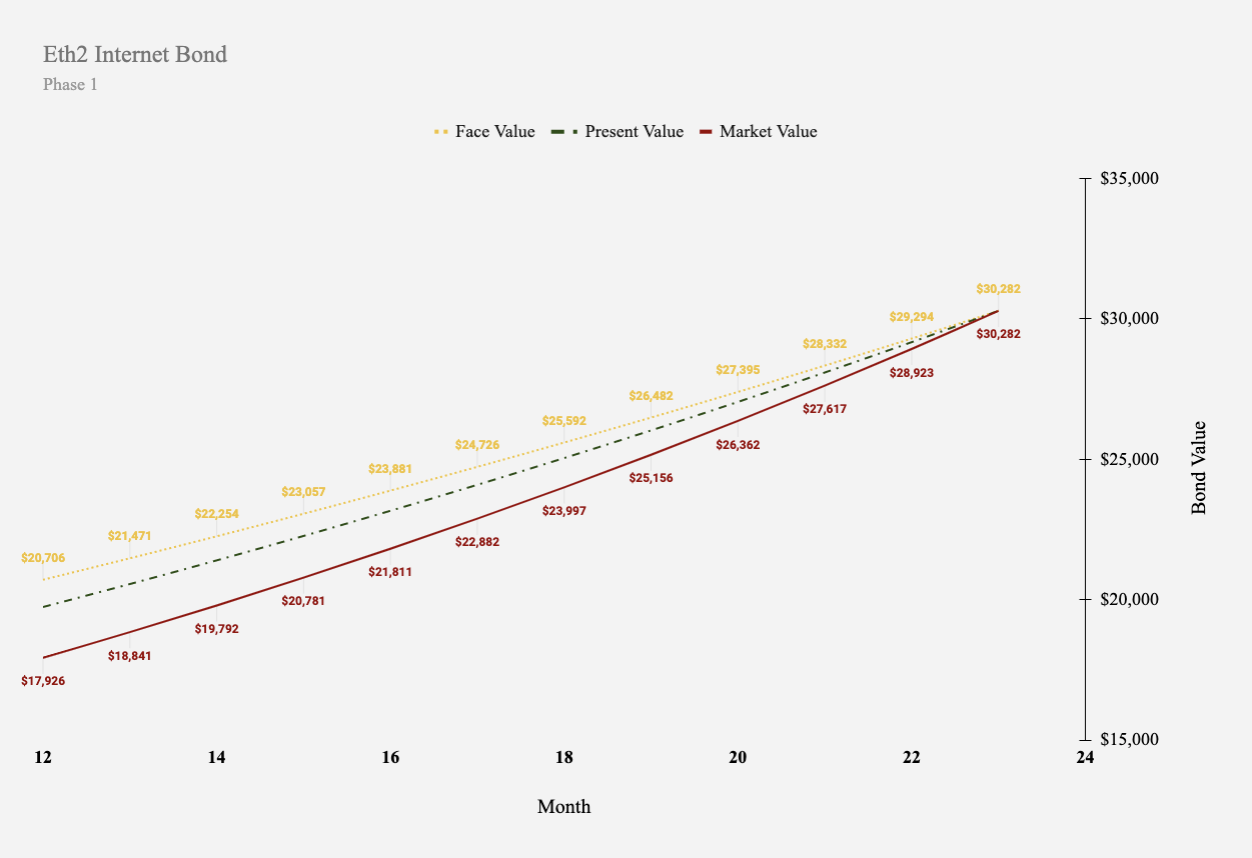
Following Phase 1, the network will transition to Phase 1.5 which features the migration of the Eth1 chain into a shard on Eth2.
In Phase 1.5, validators will be able to withdraw their deposits and claim rewards for the first time. As the Eth2 network successfully transitions, the properties of the bond changes from its deferred structure and more closely resembles a perpetual agreement with both debt and equity like characteristics.
Perpetual financial agreements, like an Eth2 Internet Bond pay rewards in perpetuity for the provision of public infrastructure and do not include maturity dates.
Conclusion
Participating in the base layer of Web3.0 represents a novel digital work agreement between global participants and decentralized internet protocols to provide trustless value transfer that the whole world can use.
The Internet bond is an entirely new asset for financial markets. It allows anyone in the world to invest, participate, and profit off an open-sourced, decentralized digital economy.
This model illustrates the relevance and value of looking and borrowing from the old to understand the new.
The Eth2 Internet Bond is here.
📑 Read the full whitepaper here
Action steps
Understand the emergence of the internet bond
Read the full whitepaper on Eth2 Economics
Don’t get caught up in Ether price analysis posts all over twitter. The fundamentals are worth diving into.
Level up on past Bankless Resources around Eth staking
Author Bio
Mara Schmiedt leads Business Development at Bison Trails, a node infrastructure provider for the decentralized economy. She previously worked at ConsenSys CodeFi as Strategy Lead where she focused on the emergence of Eth2.
Collin Myers leads DeFi Product Strategy at ConsenSys CodeFi, a blockchain application suite powering commerce, finance, and the digitization of financial instruments.
Subscribe to Bankless. $12 per mo. Includes archive access, Inner Circle & Badge.
🙏Thanks to our sponsor
Aave
Aave is an open-source and non-custodial protocol for money market creation. Originally launched with the Aave Market, it now supports Uniswap and TokenSet markets and enables users and developers to earn interest and leverage their assets. Aave also pioneered Flash Loans, an innovative DeFi building block for developers to build self-liquidations, collateral swaps, and more. Check it out here.

Not financial or tax advice. This newsletter is strictly educational and is not investment advice or a solicitation to buy or sell any assets or to make any financial decisions. This newsletter is not tax advice. Talk to your accountant. Do your own research.
Disclosure. From time-to-time I may add links in this newsletter to products I use. I may receive commission if you make a purchase through one of these links. I’ll always disclose when this is the case.