The Next Frontier of Onchain Lending

Ever wondered how much of Morpho’s activity comes from leveraged loops versus organic borrowing? Bankless Ventures just launched the first dashboard to break it down, check it out: http://dune.com/brent___brent/morpho-looping
Onchain lending has become the backbone of DeFi. Yet despite explosive growth, the underlying architecture has barely evolved since Compound v2. >99% of DeFi still runs on some variation of the overcollateralized, variable-rate model pioneered years ago.
For the world to truly operate onchain, lending must mature far beyond its current form.
What began as a simple mechanism for borrowing stablecoins is evolving into a full financial substrate. The purpose of this article is to highlight the latest breakthroughs in protocol design, credit architecture, and regulations that are pushing onchain lending towards becoming the base layer of a programmable global economy.
1. DeFi as the New Financial OS
Over the past cycle, DeFi has quietly evolved from a collection of isolated apps into a set of composable operating systems for global finance. In 2018, protocols like Aave, Compound, and Uniswap acted as discrete applications, each with its own liquidity, governance, and user base. By 2025, they’ve matured into “financial kernels:” programmable environments where liquidity, risk, and execution are abstracted into modular layers that other builders can assemble, extend, or compose into new financial systems.
In traditional software, an operating system provides three things: shared memory, standardized interfaces, and permissionless extensibility. The same pattern is now emerging in DeFi. These new “OS protocols” manage the shared state of money rather than the shared state of files. Liquidity functions as the memory layer, interest-rate curves and AMMs serve as system calls, and oracles, vaults, and governance form the coordination layer that governs execution.
Several leading protocols now embody this design philosophy:
- Aave v4 is evolving into a hub-and-spoke liquidity operating system. At its core is a governed kernel called the Liquidity Hub, surrounded by modular markets for RWAs, GHO, and permissioned pools. Liquidity is supplied once and can be deployed across all spokes under governed risk parameters, creating unified capital efficiency instead of fragmented pools. This marks a major step beyond Aave v3’s isolated-market architecture toward a fully shared liquidity layer.
- Morpho v1 and Euler v2 take the opposite route: a minimalist credit kernel with no shared liquidity, only shared logic. Each vault is its own micro-market, but all inherit the same primitive, a unified accounting and liquidation engine. Morpho v2 builds on this foundation, replacing static vaults with an intent-based, RFQ style matching layer that allows fixed-rate and variable-rate loans to coexist within a unified credit marketplace.
- Fluid represents the most vertically integrated version, a unified liquidity OS where lending, trading, and collateral all draw from the shared pool. It’s the first system that treats every dollar of idle capital, collateral, and borrowed funds as interconnected resources.
Together, these architectures signal the next stage of DeFi’s evolution. The primitive era of isolated money markets is giving way to interoperable financial systems that function more like operating environments than applications. Liquidity, risk, and governance are becoming shared infrastructure rather than product features. Whether through modular hubs, minimalist kernels, or vertically integrated engines, the endgame is the same, finance that is open, programmable, and globally composable.
2. Orderbook-Based Lending
Most DeFi lending still relies on pooled models, where all liquidity providers share risk and returns. This has advantages in simplicity and shared liquidity, but it comes at the cost of precision. Moreover, rates are algorithmically or DAO derived rather than negotiated, a stark contrast to the granularity offered in TradFi.
The next step-function unlock in lending microstructure is orderbook-based lending, where lenders and borrowers post specific offers, much like a central limit order book (CLOB) in traditional finance. This structure enables granular control over terms: fixed vs. variable rates, maturity dates, collateral requirements, and even custom risk parameters. Hybrid models are also appearing, combining pooled liquidity for depth with orderbook mechanisms for price discovery.
Just as AMMs evolved into concentrated liquidity models, lending markets are likely to converge toward these more expressive designs. However, the key difference is lending markets are built with the passive lender in mind, so the average lender will have the same experience, but the borrower will have more optionality.
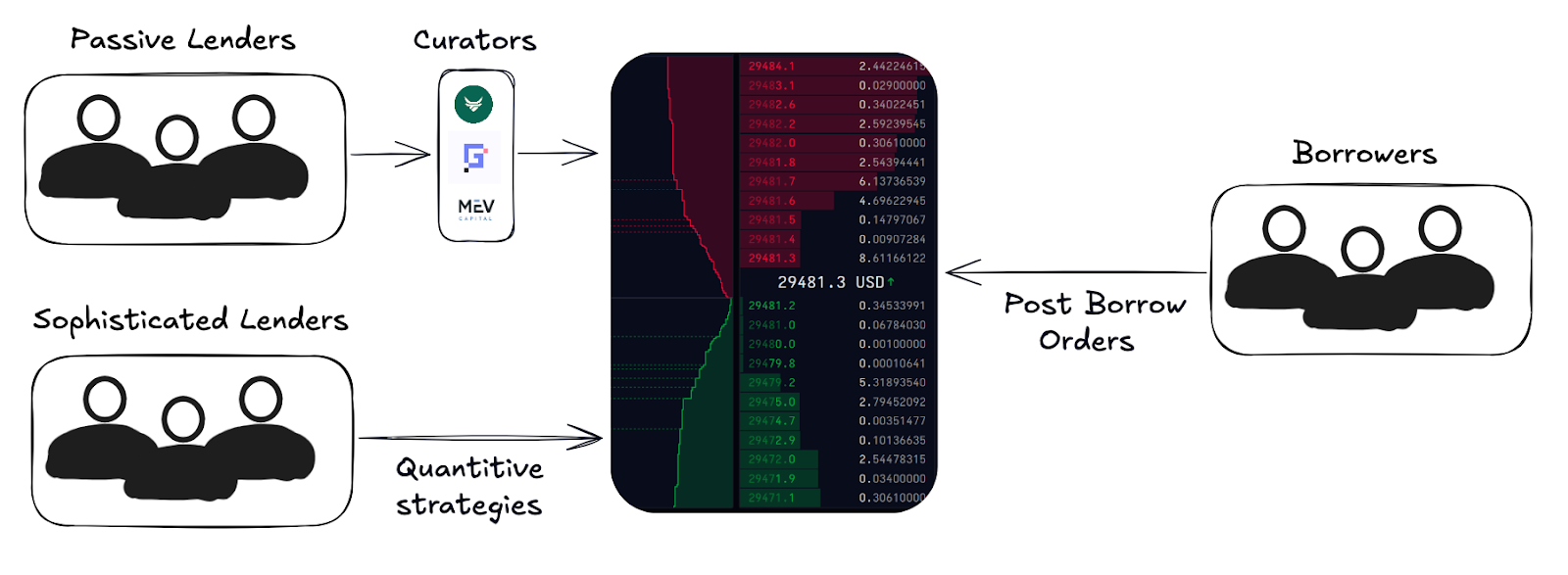
Orderbooks can facilitate both variable-rate and fixed-rate lending, but the underlying mechanics remain similar: lenders post offers, borrowers take them, and matching creates onchain credit positions. Most capital in these systems will come from passive lenders, typically deployed through curators or vault managers who aggregate liquidity and manage parameters on their behalf. Avon is pioneering a hybrid architecture that combines a central limit order book with custom strategies (isolated markets), allowing compatible orders to clear atomically, while still catering to the passive lender.
3. The Convenience Era
As alluded to above, base layer lending protocols will be entirely abstracted by a legion of consumer friendly products. Think looping, automated risk management, yield abstraction, consumer agents etc.
- Looping strategies are being abstracted into seamless, one-click products. Platforms like Contango and Loopscale already automate the process, while lending markets such as Jupiter, Euler, and Silo are beginning to enshrine these mechanics directly into their frontend.
- Yield Abstraction: To end users, lending will collapse into a single “net yield” number. The strategies beneath it will fade into the background, much like how banks hide the plumbing of overnight repos behind checking account interest. As exchanges like Coinbase integrate directly with protocols like Morpho, yield will become a table stakes UX feature rather than a complex financial operation.
- Consumer Agents: Intelligent agents will dynamically manage collateral ratios, refinancing, and liquidation protection on behalf of users. These systems will rebalance positions across protocols, optimize borrow costs, and hedge volatility in real time, turning active portfolio management into a background process
4. Ratings, Benchmarking, and Compliance
DeFi will only scale to trillions when a CFO can use it without risking their job.
No financial market matures without standards, and lending is no exception. Credit ratings, transparent benchmarks, and compliance rails form the trust infrastructure that bridges code-based markets with real-world capital.
Ratings: Just as Moody’s or S&P assess corporate and sovereign credit, independent risk agencies will emerge to evaluate DeFi vaults, protocols, and onchain credit portfolios. These ratings will quantify smart-contract risk, collateral quality, counterparty exposure, and historical performance, enabling institutional risk frameworks to map cleanly onto DeFi primitives. While I believe S&P and Moody’s are likely to dominate here as well, there are emerging players like Web3SOC, Credora etc.
Benchmarking: Standardized indices, think a “DeFi LIBOR” or “Onchain SOFR,” will allow borrowers, lenders, and treasuries to price risk and compare yields across protocols. This creates the foundation for derivative products, yield curves, and structured credit markets to form natively onchain.
Compliance: As institutions enter, embedded KYC/AML will become table stakes. Protocols will increasingly segregate liquidity into permissionless and compliant tranches, enabling regulated entities to access DeFi rails while preserving open access for everyone else. For example, Morpho v2 vaults support customizable access controls designed for institutional-grade compliance.
Together, these elements could form the institutional interface for onchain credit.
5. Beyond Overcollateralization
Today’s market is dominated by overcollateralized, variable-rate lending against crypto assets, a useful but inherently narrow niche. The next horizon for onchain credit expands far beyond that model, unlocking the full credit spectrum that powers traditional finance.
Fixed-Rate Lending: Predictable payments, defined maturities, and structured instruments are prerequisites for institutional adoption. Protocols like Morpho v2 are pioneering intent-based fixed-rate markets, while emerging designs such as Term and Tenor explore auction-driven and orderbook mechanisms that price duration risk directly onchain. In practice, Morpho v2 will likely serve both ends of the spectrum, highly liquid, orderbook-style markets on one side, and deeply customizable OTC-style quotes on the other, with curators allocating to the liquid vaults and lending desks managing the more bespoke credit exposures.
Undercollateralized Lending: Protocols like 3Jane and Wildcat are pioneering frameworks for trust-minimized, undercollateralized credit, combining smart-contract–enforced guarantees with real-world underwriting and delegated reputation.
Exotic Credit Markets: Lending is also extending to long-tail and non-traditional collateral: tokenized RWAs, exotic FX pairs, stablecoin carry trades, and even reputation-backed credit lines. These markets introduce diversification, cross-border liquidity, and new risk dimensions that mirror the complexity of global finance. A timely example is Midas’s explosive growth which highlights a two-sided demand dynamic: traditional finance seeks to channel onchain liquidity bolstered by looping, while crypto-native investors seek high yield exposure to non-correlated, TradFi instruments.
Together, these frontiers signal the evolution of DeFi from a collateral-constrained niche into a full-spectrum, programmable credit system, one capable of underwriting everything from consumer loans to sovereign debt, all settled directly onchain.
Lastly, I’d be remiss to not discuss the future of DeFi lending without mentioning the rise of curators, entities like Gauntlet, Re7, Steakhouse, and MEV Capital that actively manage liquidity, optimize yields, and shape protocol parameters. These firms are evolving into the onchain equivalents of Millennium or Citadel, deploying quantitative strategies, risk models, and dynamic liquidity management across multiple protocols.
Over the past few years, curators have earned modest performance fees and often subsidized users with incentives to attract deposits. But this is the long game. They understand that curation itself will be one of the most scalable and lucrative businesses of the next decade. Deposit-taking is simply a loss leader for distribution and data. As these firms compound scale and reputation, it’s easy to imagine them becoming $10B+ onchain asset managers with embedded influence across every major protocol.
The battle for deposits will only intensify from here. There are many hedge funds, but only one Millennium, and every curator in DeFi is competing to become its onchain successor.
Conclusion
DeFi lending is no longer an experiment in collateralized leverage; it’s evolving into the architecture of a programmable financial system. From orderbook-based credit markets and one-click looping products to institutional-grade ratings and undercollateralized frameworks, every layer of the stack is being rebuilt for scale, precision, and accessibility.
Once credit is truly programmable, finance no longer lives in institutions, it lives on the network.
Thanks to Morpho, Prince, Pierre and the BVC team for the thoughtful comments and review.
About Bankless Ventures:
Bankless Ventures is an early-stage Web3 Venture fund launched in 2023 to empower pioneers to explore the frontier of web3.
We’re currently fundraising for Fund II. If you want to invest in Bankless Ventures Fund II, you can submit an interest form as a Limited Partner (LP) here.
Disclosures:
