How to trade YFI perps on Perpetual Protocol
Dear Bankless Nation,
Perpetual contracts are the most traded derivative product in crypto. They’re responsible for hundreds of billions in volume every day.
They allow traders to open leveraged long or short positions on virtually any asset—but mostly ETH and BTC these days.
If you’re a long time reader, we’ve talked about perpetuals a few times before with dYdX and MCDEX. But there’s a new player entering the chat.
Perpetual Protocol launched on mainnet in December. What’s interesting is that they built the protocol on xDAI—allowing for faster, cost efficient trading (no gas fees once you migrate) without sacrificing much on usability. And it’s safe to say they’re succeeding. Since launching less than two months ago, the protocol has facilitated nearly $1B in volume.
Not a bad achievement in that amount of time.
Perpetual Protocol uses a novel vAMM to avoid order books, drawing similarities to Uniswap. And while they only support a few assets today, the flexibility of this design allows them to support any asset on Ethereum, so long as it has a price oracle.
There’s something brewing here. So it’s worth checking out.
Here’s what you need to know about Perpetual Protocol and how to trade the YFI perp.
- RSA
Tactic Tuesday #77: How to trade perpetual swaps on Perpetual Protocol
Guest Writer: Weiting Chen, Growth Manager at Perpetual Protocol
Before diving into the tactic today, we need to do a quick recap on perpetual contracts and how they work:
The perpetual contract is a derivative that enables you to speculate on an asset’s price without the need to hold the actual asset. Users can open a leveraged long position if they expect the underlying asset’s price (of a perpetual contract) to go up, or a short position if they expect the price to go down.
Nowadays, the perpetual contract is the most-traded derivative in crypto, with billions of dollars in trading volume generated each day.
In this tactic, we’ll start with explaining what Perpetual Protocol is, how it works, dive into historical growth, and why it’s different from its competitors. Lastly, we’ll walk you through how to trade the YFI perpetual contract on the protocol without paying gas fees.
- Goal: Learn how to trade YFI perpetual contract on Perpetual Protocol
- Skill: Advanced
- Effort: <10 minutes (if you use Metamask or Ledger hardware wallet)
- ROI: Variable - depending on how well you trade
⚠️ Disclaimer: Leveraged trading is risky and not recommended for beginner traders. Please rationally judge your investment ability and make decisions prudently once you’re well informed about how perpetuals work. Perpetual markets are not available in the U.S.
What is Perpetual Protocol?
Perpetual Protocol enables trading for on-chain perpetual contracts completely gas free. The protocol leverages xDAI for fast, cost efficient trading and virtual automated market makers (vAMMs), allowing traders to open long or short positions with up to 10x leverage without the need for a counter party.
Better yet, in the future, anyone can create and run perpetual markets and get a cut of the transaction fees, similar to the LPs on Uniswap.
How does Perpetual Protocol work?
As the “virtual” part of vAMM implies, there are no real assets stored inside a vAMM—the protocol merely uses the vAMMs as a tool for price discovery rather than facilitating token swaps.
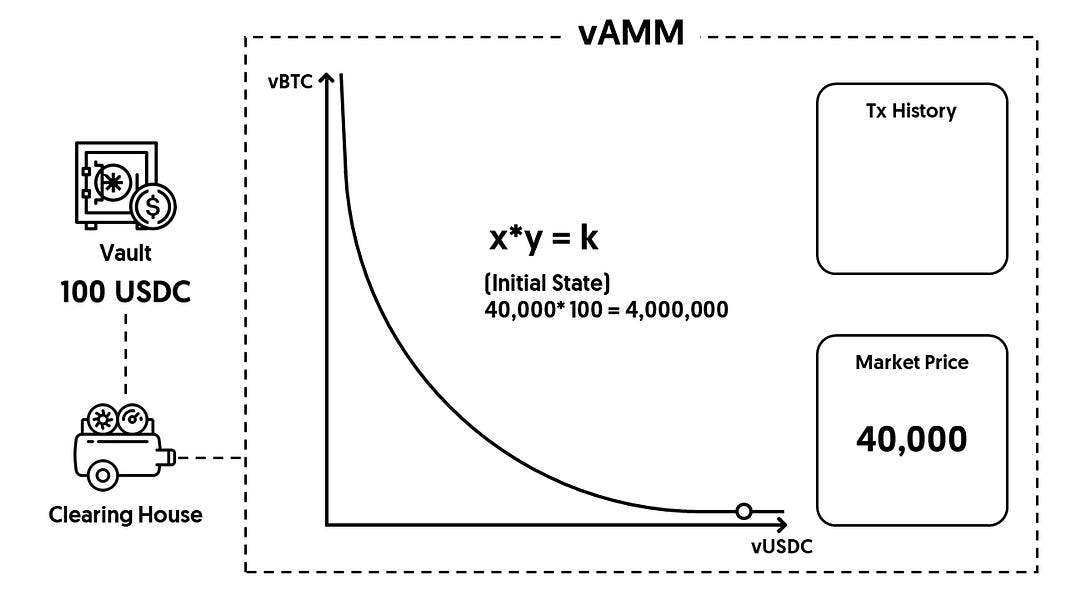
Let’s say we have a trader Alice who wants to use 100 USDC as the collateral to open a 10x leveraged long BTC position. As the first step, she needs to deposit 100 USDC into the Vault (the smart contract that stores real assets from traders).
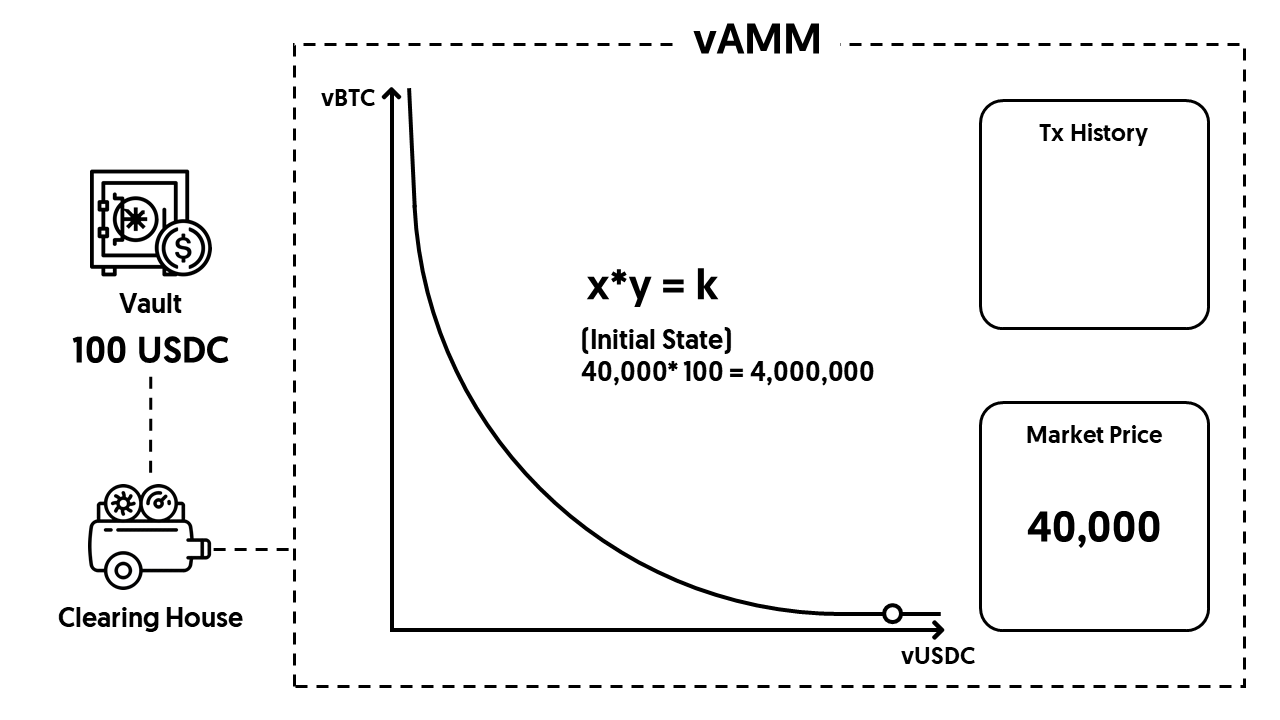
Next, the Clearing House, a smart contract that manages traders’ positions on Perpetual Protocol, will mint virtual assets (or “synthetic assets”) and put them into a vAMM. In return, this vAMM will calculate the size of the position that this trader will get based on the constant-product curve (x*y=k). This is the same pricing curve used by Uniswap!
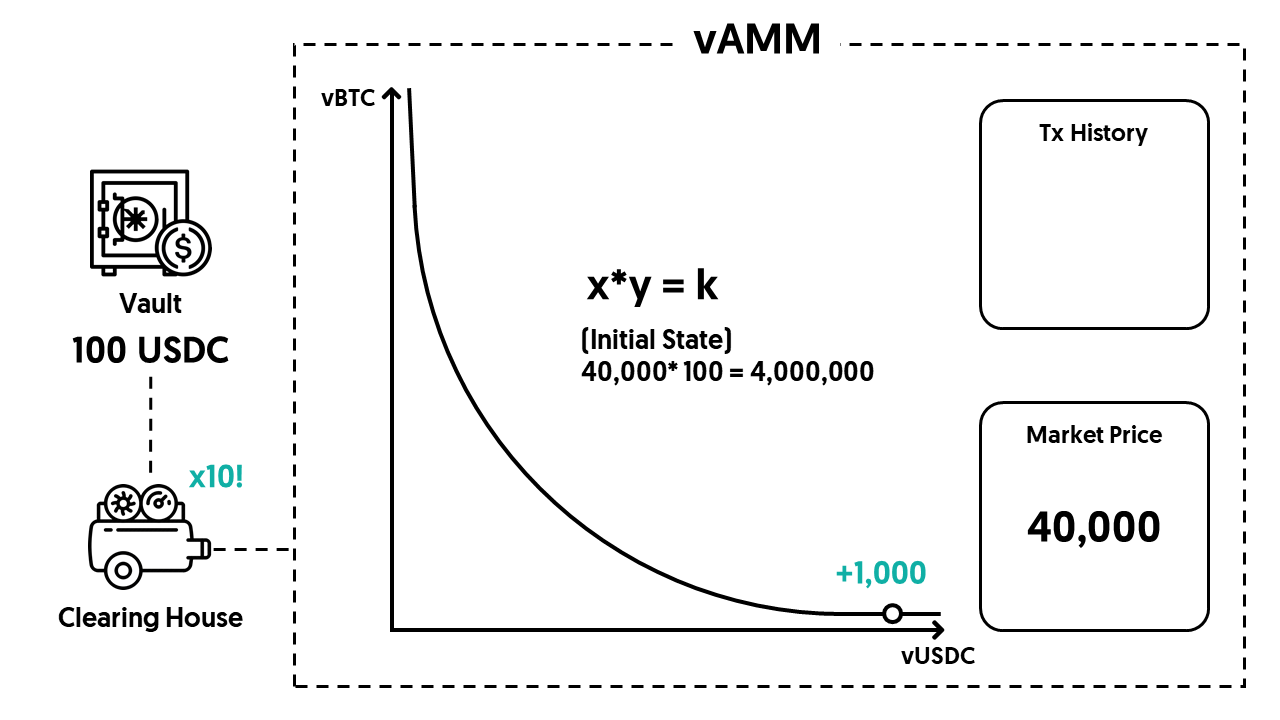
In our example, since Alice uses 100 USDC and 10x leverage to open a long position, the Clearing House will mint 1,000 positive vUSDC (negative if it’s a short position) and put them into the vAMM.
We have the above step (compared to directly putting the deposited USDC into a vAMM) because we need to apply the leverage and the direction (long or short) to the collateral.
Back to our example, the market price of BTC is 40,000 USDC, and there are 10 virtual BTC and 400,000 virtual USDC set inside this vAMM as the initial state.
⚠ Reminder: there are no real assets inside the vAMM - the 10 vBTC and 400K vUSDC set as the initial state are just two numbers stored in the vAMM used to calculate the derivative’s price.
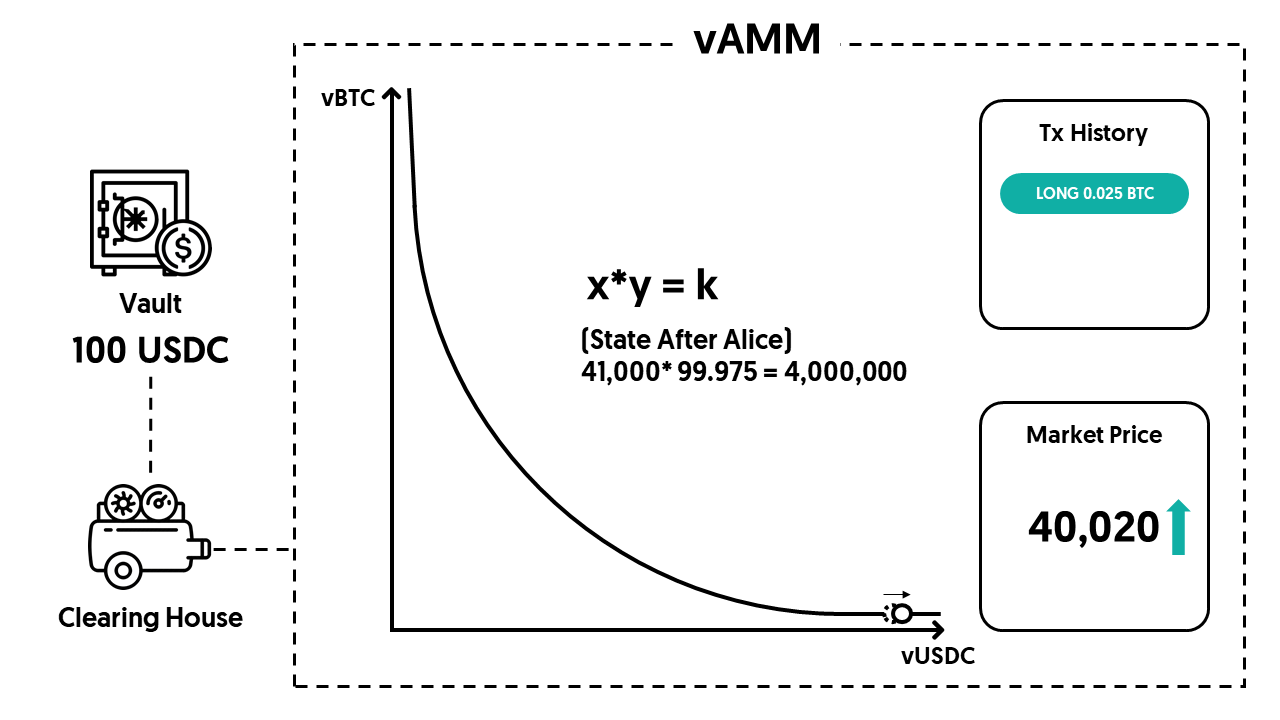
After Alice opens her position, she’ll receive a virtual position whose price is determined by the constant-product curve (x*y=k) in the vAMM. Alice now has a position worth 0.025 BTC after this trade (negative 0.025 if the direction is short).
You can check this sheet to see the price movement in different scenarios, like what would happen if another trader joins, or check our documentation to know more.
Price alignment mechanism for a perpetual contract
One common question that people ask after reading through the explanation above is, what will happen if everyone just opens long positions on a vAMM?
First it’s important to understand that since these are derivatives, the price of a perpetual contract isn’t necessarily the same as the spot price of the underlying asset.
That’s why if everyone opens a long position on a vAMM (or a perpetual contract exchange in general), the price of the derivative will keep going up, which creates an opportunity for arbitrageurs to open short positions to push the price down.
What’s more—to further drive the price of a perpetual contract (called the “mark price”) toward the spot price of the underlying asset (the “index price”), derivatives exchanges typically adopt a mechanism known as funding payments to incentivize traders to take the less popular side.
On Perpetual Protocol, funding payments are made once per hour.
Back to our initial question—if everyone opens a long position and assuming there is no arbitrageur and the spot price of the underlying asset stays the same, then during the funding time (the time that funding payment takes place), long positions holders will pay a funding payment to the vAMM, which will directly go to the Insurance Fund (more on this later). On the flip side, if it’s the turn for a vAMM to pay the funding payment, it will pay it from the Insurance Fund.
How is Perpetual Protocol different from other exchanges?
There are more and more platforms offering perpetual contracts, so in this section, let’s highlight the main differentiators for Perpetual Protocol:
1. Flexible Liquidity
In light of the adoption of vAMMs, Perpetual Protocol can adjust the liquidity of a vAMM (the “K” in the constant-product curve) dynamically since there is no real asset stored inside a vAMM. Remember: they’re synthetic assets! Right now, the K is manually set and adjusted by the team that develops the protocol; in the future, one can imagine the liquidity (K) automatically increases as there is more open interest on a perpetual market.
This characteristic is also a critical difference between Perpetual Protocol and other orderbook-style exchanges, which rely heavily on market makers to provide liquidity.
2. Support for Any Asset
If it has a price feed—no matter if it’s from Chainlink, Band, or Uniswap—Perpetual Protocol can create market for it. The protocol only needs an on-chain price feed once to calculate funding payments. In addition, since there are no real assets stored inside the vAMMs, we don’t need actual BTC, gold or other asset being traded.
This characteristic makes the protocol quite different from other exchanges that rely on liquidity providers or settle in different assets.
Historical Usage
Perpetual Protocol launched on December 14th, 2020. Here are some stats since genesis:
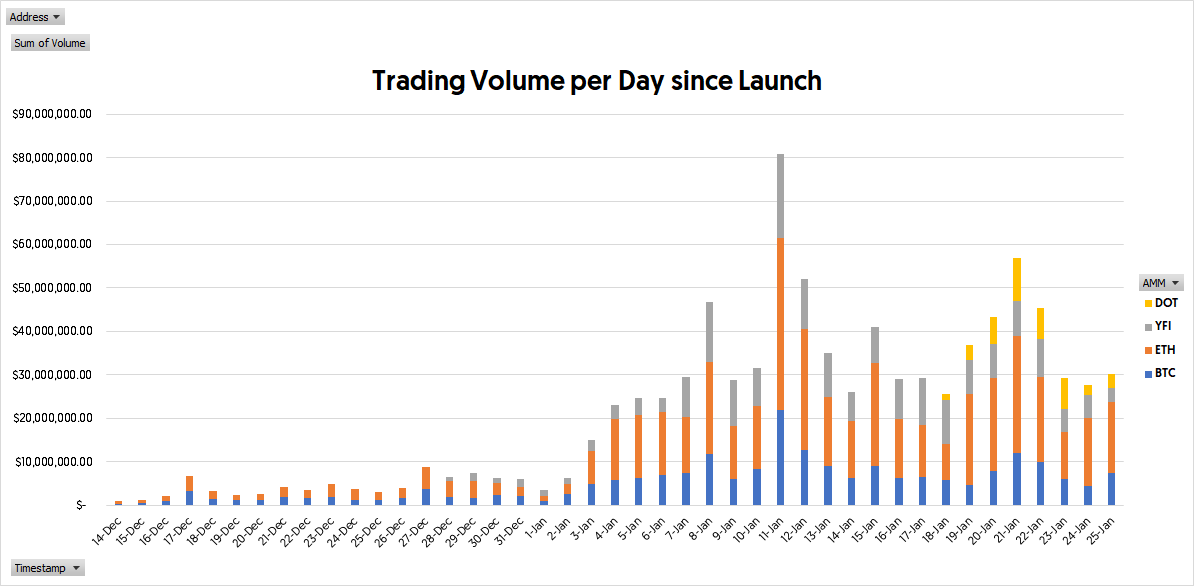
Daily trading volume has peaked to over 80M USDC and with an average of over 20M per day. We believe the trading volume will continue to increase as 1) more pairs are on the protocol and 2) as more order types are supported (as of today, the main trading venue only supports the market order). Currently, we list one new pair around once per week through the governance process.
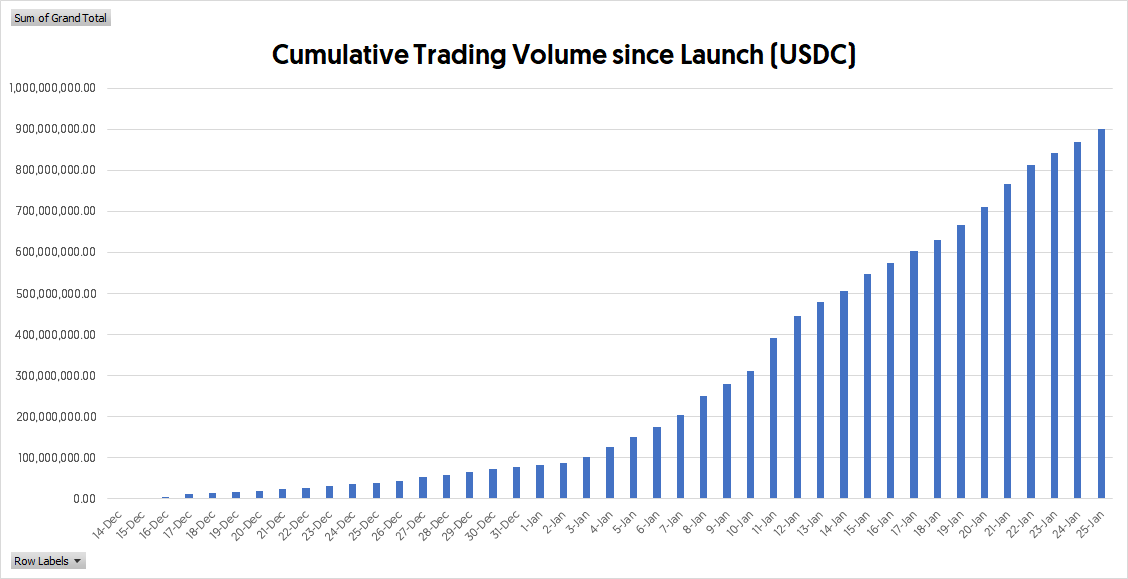
The cumulative trading volume hits 100M USDC within 1 month after the protocol’s launch, and is closing in on $1B as you read this. Meaning, Perpetual Protocol has reached 1 billion USDC cumulative trading volume in less than 2 months.
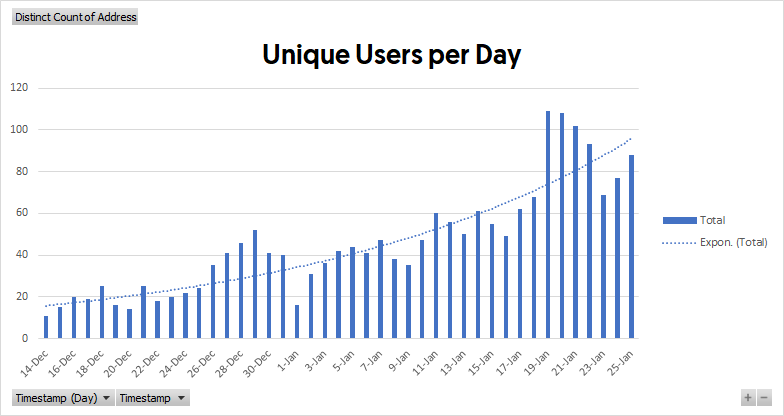
Despite the fact that the price of BTC shoots up from 19,000 USD to over 40,000 USD (and then later fallbacks to 34,000 USD), the liquidation process on the protocol has worked well: in a time span of 1.5 months, we have 49 liquidations on the BTC market, and only one of which creates a sub 0.001 USDC loss to the system (the root cause of that loss is from a dust position that is manually closed by a user). As such, we’re considering to increase maximum leverage soon, which is currently capped at 16x.
If you want to dig into more numbers, you can check out the dashboard on DuneAnalytics or query the on-chain data on the subgraph.
The role of the PERP token
Perpetual Protocol features a native token (PERP) which underpins the system for two key actions:
1. Backstop Asset
Two scenarios could incur a loss to the protocol:
- Untimely Liquidation: Keepers fail to liquidate under-collateralized positions.
- Funding Payment: When a perpetual market isn’t balanced, and a vAMM needs to pay funding.
When either one of these scenarios happens, the funds inside the Insurance Fund will firstly be used to repay the loss (50% of the transaction fees will go to the Insurance Fund). If the Insurance Fund is depleted, the system will mint PERP and sell it on the market to repay the debt.
2. Fees & Governance
PERP token holders can stake their tokens on the protocol, in return, we can receive staking rewards (in PERP) and a cut of the transaction fees (in USDC). Also, stakers can vote with their staked PERP on the governance portal to determine important decisions for the protocol, such as a new market to list or the transaction fee (%) to charge, etc.
How to trade YFI perp on Perpetual Protocol
If you’re interested in trading perpetual swaps on Perpetual Protocol, we got you covered. Let’s learn how you can trade the YFI perp in a few steps.
⚠️ Due to local regulations, users from certain jurisdictions, like the U.S., cannot access the protocol through our website. If you’re one of them, you can follow this guide with our testnet on Rinkeby instead (remember to switch the network setting on your wallet to Rinkeby testnet and click “Request USDT” to get some test money).
Step 1: Connect your Wallet
Head to perp.exchange and connect your wallet by clicking the “Connect” button in the upper-right corner.
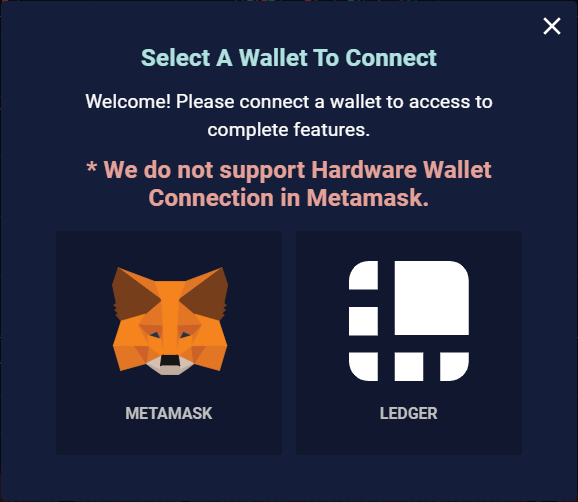
At the time of writing (Feb 2nd, 2021), the website only supports Metamask and Ledger to trade with, but Trezor support is coming soon!
Step 2: Load up your USDC Balance
Once your wallet is connected, the next thing you need to do is to top-up your USDC balance on the protocol. You can start the deposit process by merely clicking the “Deposit” button in the upper-left corner.
There are four steps in the deposit process:
- Confirm the deposit amount. There is no minimum deposit amount—you can deposit as many USDC as you like. In our tutorial here, I’ll deposit 500 USDC.
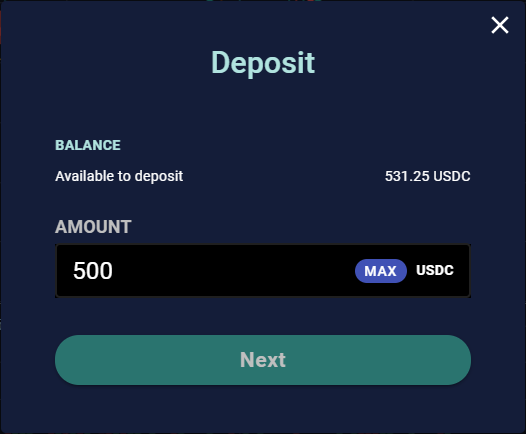
- Approve our smart contracts to transfer your USDC (on Ethereum). As mentioned earlier, since the entire protocol runs on xDai Chain, we need your permission to “migrate” your USDC—that’s what the protocol is doing in this step. Click the “Approve” button and submit the transaction.

📑 You only approve our smart contracts once.
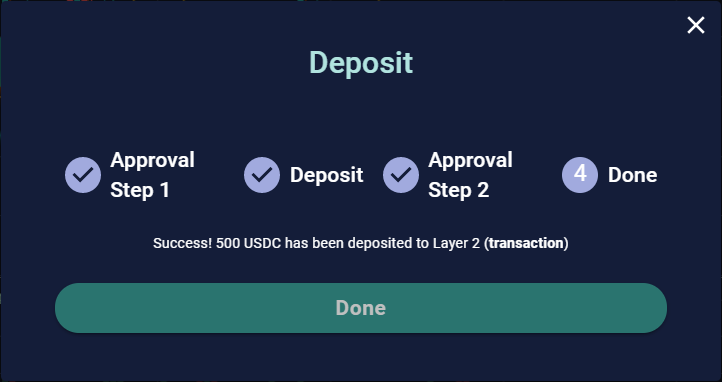
- Deposit USDC to the Perpetual Protocol smart contract (on Ethereum). Once the approval transaction is confirmed, you need to deposit USDC into our smart contracts on Ethereum so that we can start the migration to xDai Chain.

As soon as your deposit transaction is confirmed on Ethereum (Layer 1 in the screenshot above), it’s migrate the deposited USDC to xDai Chain (Layer 2 in the screenshot above), where the entire Perpetual Protocol resides.
⛽ You do NOT need to pay any gas fees after this step - Perpetual Protocol covers them for you.
- Approve our smart contracts to transfer your USDC (on xDai Chain). Till this point, your USDC has been migrated on to xDai Chain. As the last step before trading, you need to approve our smart contracts on xDai Chain so that they can use your USDC as the collateral for your positions.

After clicking the “Approve” button, you’ll be “welcomed” by a warning sign on your Metamask (as the screenshot below shows):
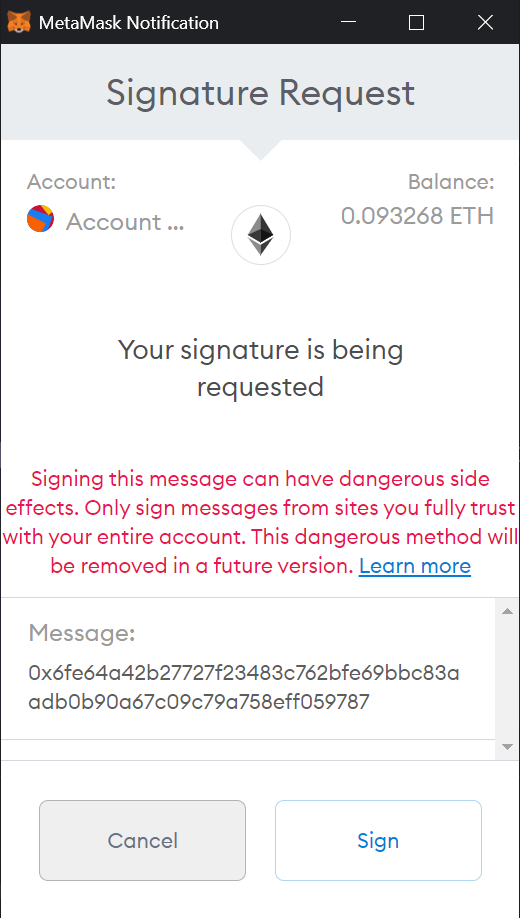
Hold your horse mouse! Let’s explain what that warning is before you leave the page:
Whenever you want to use Metamask on a different chain, you need to change the RPC settings on your Metamask, which is a significant hurdle to the adoption of scaling solutions.
To overcome this hurdle, we use meta transactions to send the messages signed by the users (eth_sign and EIP-712) to xDai Chain on behalf of them. By doing this, users can interact with our smart contracts on an entirely different chain without knowing the underlying mechanisms. AggroTrader on Twitter puts it well here
However, the downside of this approach is that Metamask will always show a warning sign (the one you saw) when an app uses the eth_sign function. But since you only need to approve the spending of USDC on xDai Chain for our smart contracts once, you’ll only see this warning for one time (we use EIP-712 signing methods for other interactions on the platform).
Step 3: Open a Long Position
I hope the explanation above convinces you to click the “Sign” button. But now that we’re on xDAI, we can move on to the main event: trading a perpetual.
Since we’re looking to trade the YFI perpetual contract in this tactic, you need to click the dropdown menu in the upper-left corner and choose “YFI/USDC”.
Once the market information displays correctly, you can now open a long or short position to speculate on the price movement of the YFI token. I choose to open a 0.1 YFI long position with 10x leverage.
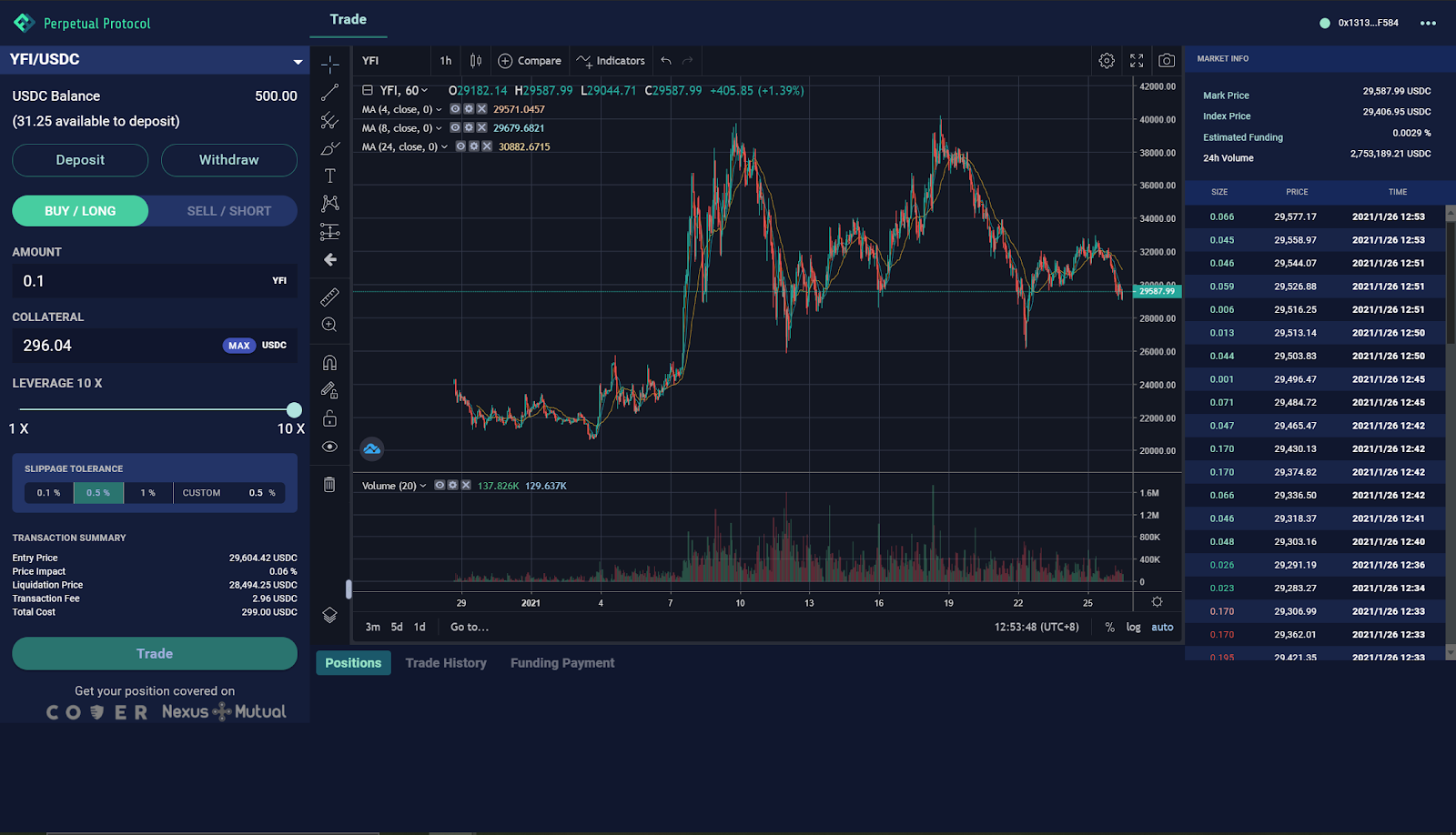
The protocol charges 0.1% transaction fee for each trade. Right now, 100% of these fees are directed to the Insurance Fund. When the staking function is live, 50% of the transaction fees will be shared among all of the stakers.
📑 On Perpetual Protocol, the price of a derivative that a trader will get is determined by the constant-product curve (x*y=k) in a vAMM. As such, the larger your position size is, the worse price you’ll get (akin to the pricing mechanism on Uniswap).
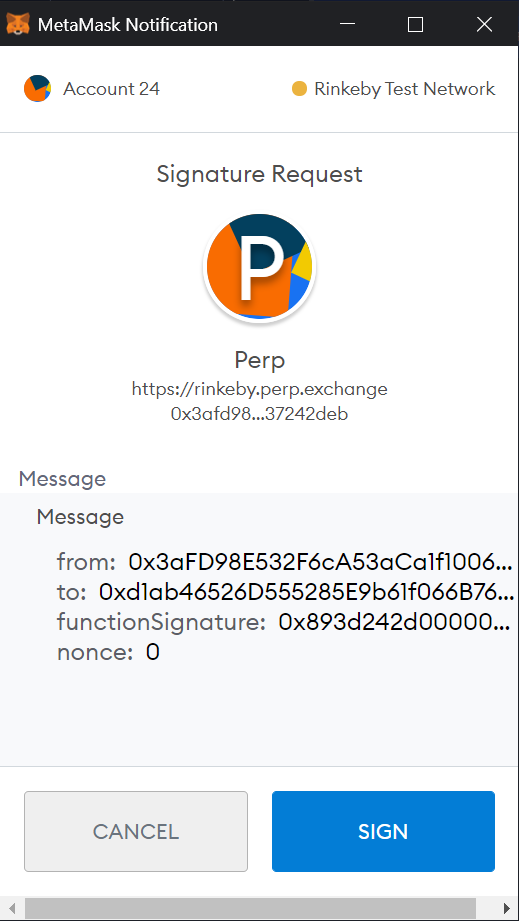
You’ll see a similar message as the image above shows on your Metamask after clicking the “Trade” button. The reason why we have this confirmation is that, for the sake of UX, we use meta transactions to send users transactions on behalf of them to the xDai Chain, where their signed transactions will be executed at.
Currently, we only support market orders, so your order will immediately be executed once you sign the transaction on your wallet.
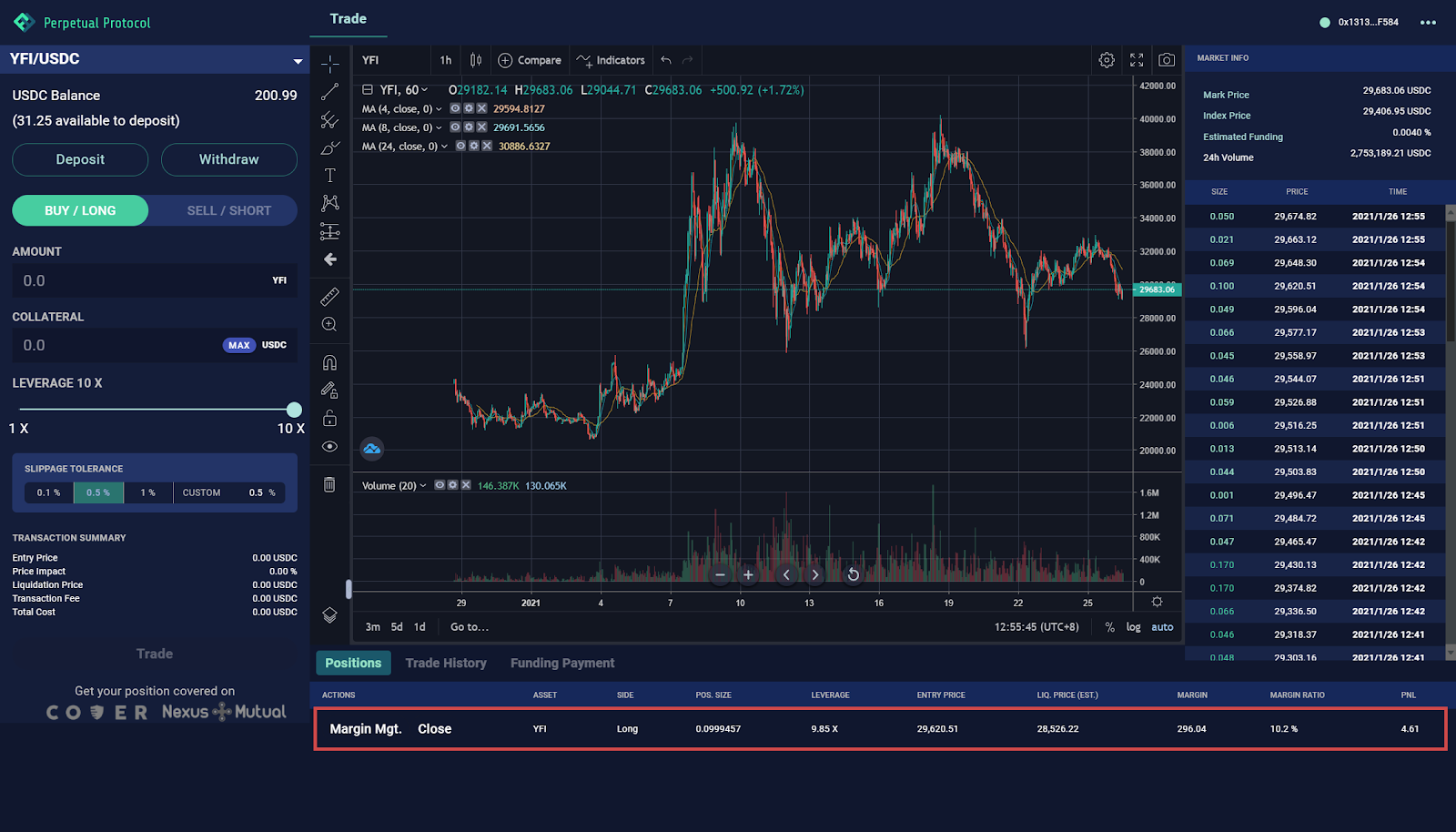
⚠ The limit order, stop-loss order, and take-profit order are being made, and they should be out within a few weeks after the release of this article.
Step 4: Close a Position
You can close your entire position anytime merely by clicking the “Close” button (and signing on your wallet afterwards):
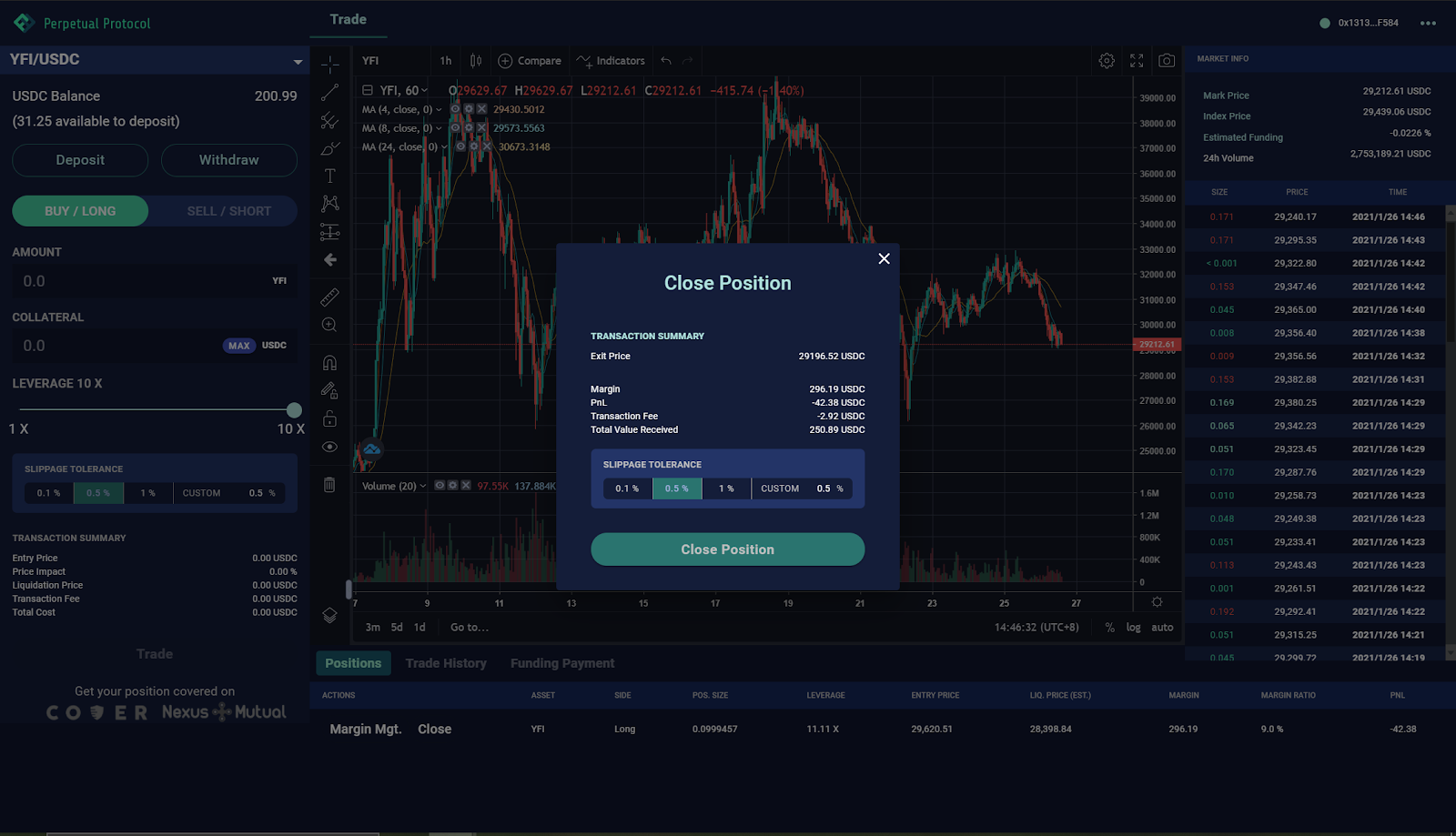
If you just want to do a partial close, the only way to do it now is to manually create an order with an opposite direction of your active position and an order size that you want to close with.
That’s all we have today! You’ve leveled up on perpetual swaps, Perpetual Protocol, and learned to trade YFI derivatives on Ethereum.
Thanks for reading this walkthrough, and we hope you learn something new from it.
For any other questions surrounding Perpetual Protocol, come join the Discord!
Action steps
Go long or short with the BTC, ETH, DOT, SNX, or YFI perp (or try on Rinkeby)
Learn more about how Perpetual Protocol’s vAMM works
Read previous Bankless resources on perpetual contracts
Author Bio
Weiting Chen is the Growth Manager at Perpetual Protocol. Before being one of the Perpetual Protocol’s members, he led a project in a centralized exchange based in Bangkok to build a digital bank with interests coming from various DeFi protocols.