How Bitcoin Builds DeFi

Dear Bankless Nation,
Bitcoin has a market cap of ~$400 billion.
As the OG grandaddy crypto, that’s quite the feat.
Bitcoin’s bare-bones design birthed a secure, decentralized, and censorship-resistant network that is widely trusted by the masses.
Unfortunately, that design also comes at a tradeoff — the network has no smart-contract capabilities on the base layer.
That means that asides from serving as an inflation hedge, much of the value on Bitcoin is currently idle capital. This is unlike networks with smart contracts where capital can be transferred and used in creative ways.
But just like ogres, onions, and any other blockchain, Bitcoin has layers.

That’s where DeFi and smart contracts are being built.
Lightning Network, Stacks, RSK and Liquid are just a few of the early examples of this.
Muneeb Ali of Stacks & Trust Machines gives us a big picture overview of the Bitcoin DeFi landscape today.
- Bankless team
WRITER WEDNESDAY
Guest Writer: Muneeb Ali, Founder of Stacks

It’s Time For Bitcoin Layers
Bitcoin has established itself as the store of value in the crypto industry.
However, Bitcoin is mainly held passively in wallets and cold storage. It is not considered a productive asset.
Currently, any active use of Bitcoin for trading or lending primarily happens through centralized companies like Coinbase or BlockFi.
There is a tremendous opportunity to finally enable decentralized use cases for Bitcoin that can make it a productive asset by actively deploying BTC in smart contracts.
During the last bull market, we saw the rise of web3 — DeFi, NFTs, and other use cases. Most of these experiments are currently happening on Ethereum and newer L1s like Solana and Avalanche.
With it, the developer and app ecosystem on the Bitcoin side remains relatively small compared to Ethereum. This is because the Bitcoin base layer is simple and does not support complex applications. Bitcoin follows simple design architecture to keep the base layer secure, immutable, and durable.
Despite its simplicity, Bitcoin remains the largest asset class in the industry. Even in today’s bear market, there is $400 billion of capital that’s just sitting there waiting to be unlocked by developers in new use cases and applications.
In this article, we discuss the future of Bitcoin, how this ecosystem will be built, and highlight some projects that are bringing new use cases to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
This all happens through Bitcoin layers, which will unlock a new wave of innovation that can massively expand the Bitcoin economy.
DeFi is coming to Bitcoin today.
Here’s how.
The Role of Bitcoin Layers
Bitcoin was designed to scale in layers.
Satoshi Nakamoto wrote about this possibility in 2010:
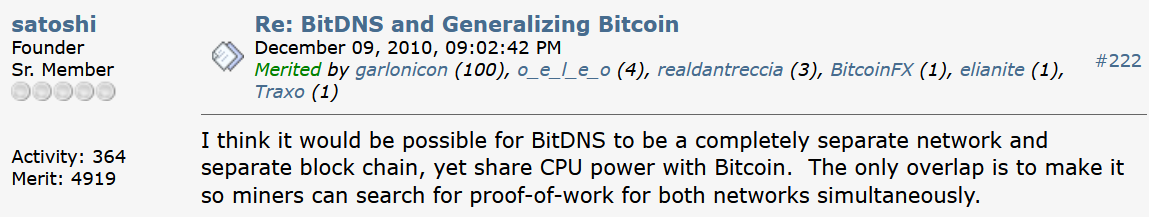
Bitcoin L1 is for settlement, not payments.
For example, payments can happen on faster, cheaper layers like Lightning and then settle back to the L1.
Similarly, other Bitcoin layers like RSK or Stacks introduce smart contracts (full execution environments) without changing the base layer.
There is a clear separation between the roles of Bitcoin and its layers.
Experimentation happens on higher-up layers. The base layer optimizes for decentralization and durability; it focuses on being a store of value.
Bitcoin becomes more productive on the higher layers while not sacrificing decentralization and other valuable characteristics (like censorship-resistance) on L1.
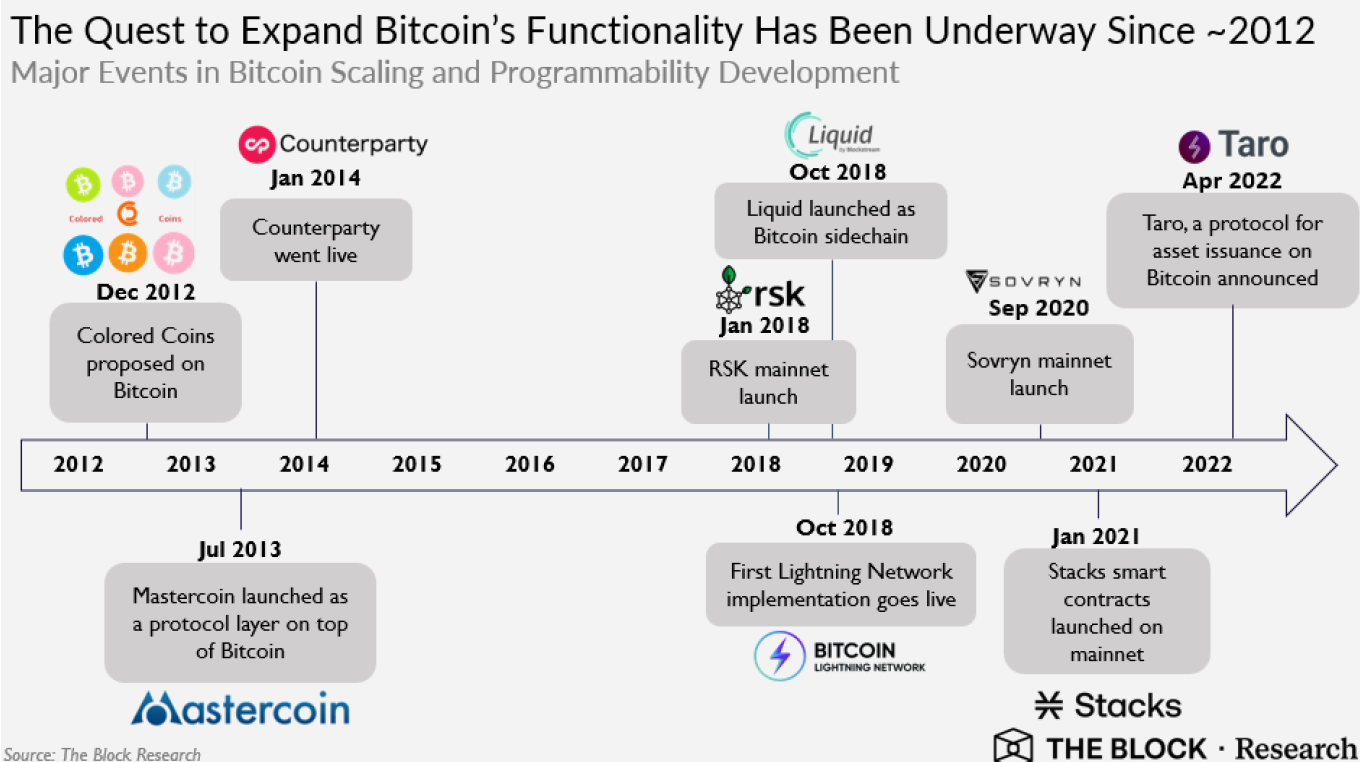
What Bitcoin Layers Exist Today?
Four main Bitcoin layers exist today: Lightning, Stacks, RSK, and Liquid.
Each layer is at various stages of maturity and traction. This research report by the Block, published in June 2022, gives an overview of the current state of Bitcoin layers.
1. Lightning Network
Lightning is a layer for scaling payments on Bitcoin.
Lightning is focused on faster and cheaper payments in a trust-minimized manner. Payments occur off-chain through specific channels; ultimately, the channel does the final settlement on the Bitcoin main chain.
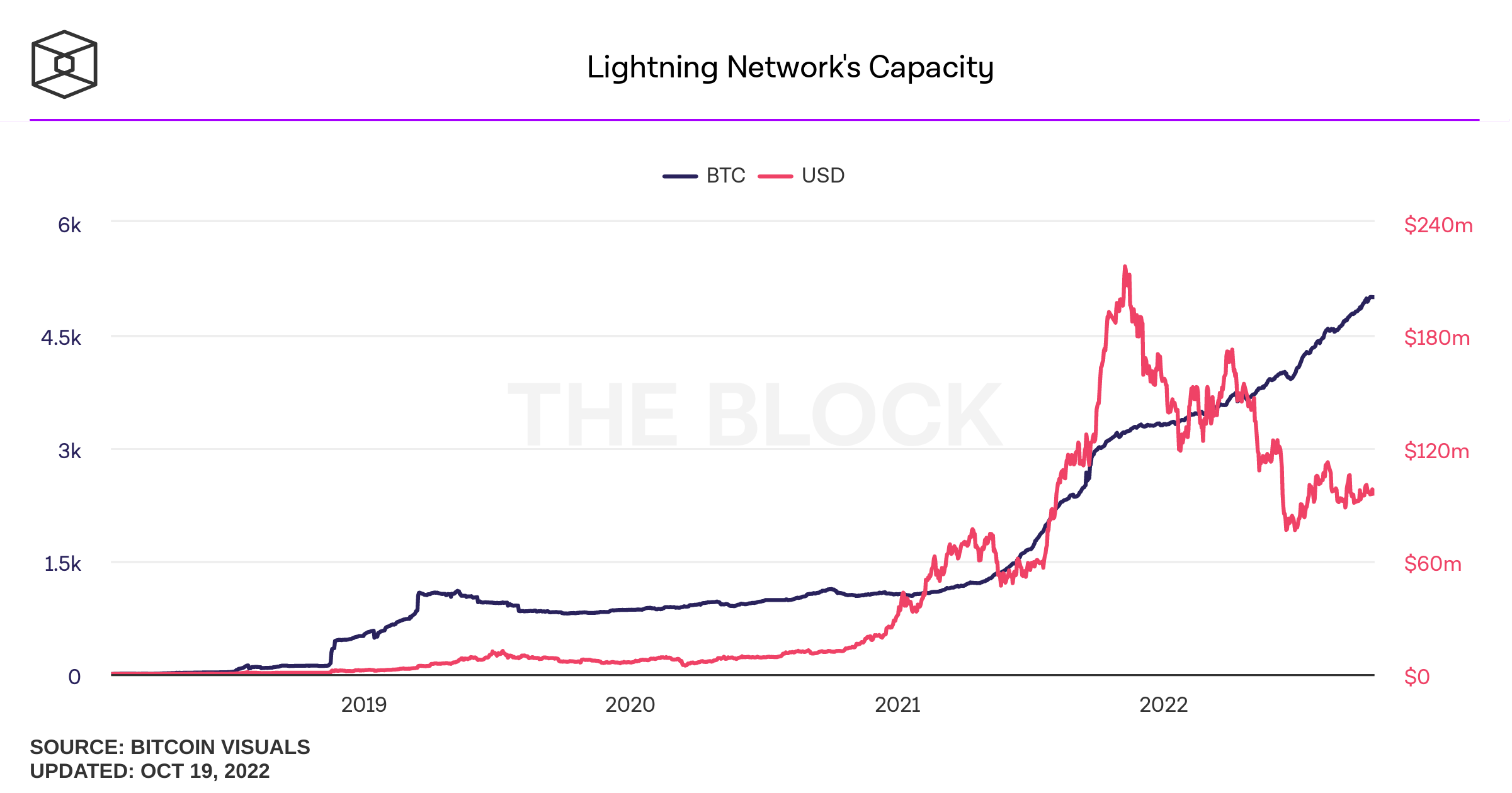
Lightning does not have an execution environment or a global ledger; it has a peer-to-peer design focused on payments. Today, the Lightning network channel capacity has recently crossed $100M, with 17,000+ active nodes and millions of payments processed.
2. Stacks
Stacks is a Bitcoin layer for smart contracts.
It has a full execution environment, and any application that can be built on chains like Ethereum or Solana can be built on the Stacks layer.
Transactions on Stacks settle on Bitcoin automatically every Bitcoin block.
Contracts on the Stacks layer can read and react to Bitcoin transactions, and there is ongoing work to easily move BTC in and out of the Stacks layer in a trustless way. Developers have recently published 5,000+ contracts on Stacks, and contracts (e.g. stacking) have $150M+ capital locked earning BTC rewards.
3. RSK
RSK is a Bitcoin layer that is merged-mined with Bitcoin (simultaneously mining RSK blocks together with Bitcoin blocks) and brings EVM-compatible smart contracts.
RSK uses a federation of hardware wallets to do a peg in and out of BTC to RSK.
4. Liquid
Liquid is a federated layer with Bitcoin peg in and out functionality managed by the federation. Liquid currently has asset issuance functionality but not a full execution environment (unlike Stacks and RSK) yet.
Improving Bitcoin Layers
Other than the Bitcoin layers discussed above, some scripts at the Bitcoin mainchain, like DLCs (Discreet Log Contracts) and Taproot, can enable limited programming ability directly at the Bitcoin base layer (ex: Atomic Finance).
Taproot and DLCs can also enhance the functionality of Bitcoin layers by improving the interaction between the base layer and the various Bitcoin layers.
Taproot or DLCs should not be confused with full execution environments like EVM; they have a different scope but are complementary to Bitcoin layers like Stacks and RSK, which have full execution environments (EVM for RSK and Clarity VM for Stacks).
Why Bitcoin’s Solid Foundation Matters
Bitcoin focuses on durability and decentralization. Users can take Bitcoin software from as far back as 2013 and run it unmodified to use with the current chain.
Further, normal users with laptops and home internet connections can run full nodes of Bitcoin unlike many new L1s where it’s not possible given high hardware or bandwidth requirements for full nodes.
Bitcoin has a grassroots movement, and its culture rejects any points of centralization in the ecosystem — at least on the base layer. The Bitcoin community has a careful and risk-averse approach to network upgrades, and changes to the code base happen slowly and carefully.
Bitcoin has the largest crypto capital base, biggest brand name, and community. Bitcoin has been around the longest, and given the Lindy Effect is most likely to survive for decades to come.
It has reached a level of decentralization and security budget that is very difficult for any actor to shut down the network or launch significant attacks against it. Bitcoin code base carries the largest live bug bounty on the planet; anyone in the world can discover an exploit to steal money, and yet for 10+ years, we have not seen exploits or hacks on the live network.
Challenges & Opportunities for Building on Bitcoin
In my opinion, successful experiments and valuable applications in crypto will eventually gravitate towards using BTC capital and to benefit from the security of Bitcoin settlement.
There is some evidence of it already happening, e.g. after the popularity of .eth names, recently 100,000 .btc names were registered on Bitcoin through the Stacks layer, with secondary market trading happening on Bitcoin NFT exchanges like Gamma.
Further, Zest Protocol is bringing on-chain Bitcoin loans against corporate balance sheets to the Bitcoin ecosystem, similar to how Maple Finance brought this functionality to Ethereum.
Often, developers are interested and excited by the idea of building on Bitcoin.
However, they quickly realize that the dev tooling and infrastructure need more work and that speed and performance issues are very real and need to mature further.
There are complex technical challenges like a Bitcoin peg out from layers that need to be solved before we can progress towards successful apps from crypto getting implemented at scale and gaining mainstream user adoption.
Undoubtedly, Ethereum has the largest developer community in crypto, and newer L1s such as Solana and Avalanche are attracting more developers than Bitcoin.
However, we have also seen how developers and capital can quickly move from one chain to another. The developer and user experience on various Bitcoin layers is still maturing, and recently there has been significant capital injection into companies building on Bitcoin — Trust Machines raised a $150M round, and LightSpark raised a large round in 2022, respectively.
Bitcoin is not a rock; it is a programmable store of value and will become even more valuable through the introduction of Bitcoin layers.
While there’s a long road ahead, DeFi on Bitcoin is being built today.
You can try it out for yourself. Check out our essential guide to Bitcoin DeFi below.
Action steps
Author Bio
Muneeb Ali is a co-founder of Stacks, a Bitcoin layer for smart contracts. He is the CEO of Trust Machines, a startup building Bitcoin applications. He received his PhD in distributed systems from Princeton. A more detailed bio is here.